Mainstream theories of social inequality frequently compartmentalize experiences, but inequality rarely works that way in real life. Instead, individuals are comprised of many different identities at once, and these identities will interact with one another in unique ways.
Furthermore, multiple systems and institutions are simultaneously at work in a given society. So, for instance, simply focusing on race as an identity and white supremacy as an institution ignores the fact that race will be experienced differently by people with different genders, ages, sexualities, abilities, and nationalities.
This schema is known as intersectionality, and it is a concept that emerges out of Black feminist thought.
In animal studies, vegan feminists employ this framework to argue that one’s life chances will be shaped, not just by one’s race, class, or gender, but also by their species. Vegan feminists also recognize the influence of an additional system….human supremacy.
For animals, we want to be thinking about how historical constructions of race, class, gender, and other identities shape how animals are thought about and how they are treated. Female-bodied animals, for example, are more likely to be exploited in the food industry given their ability to produce breastmilk, eggs, and babies. In another example, some animals that are associated with communities of color, like pit bulls, are more susceptible to punitive and often lethal breed restriction policies.
Meanwhile, for human justice theorists, it will be important to recognize how human oppression is always shaped by processes of species inequality. For instance, women and people of color have historically been animalized, and this animalization is inseparable from the oppression they face today.
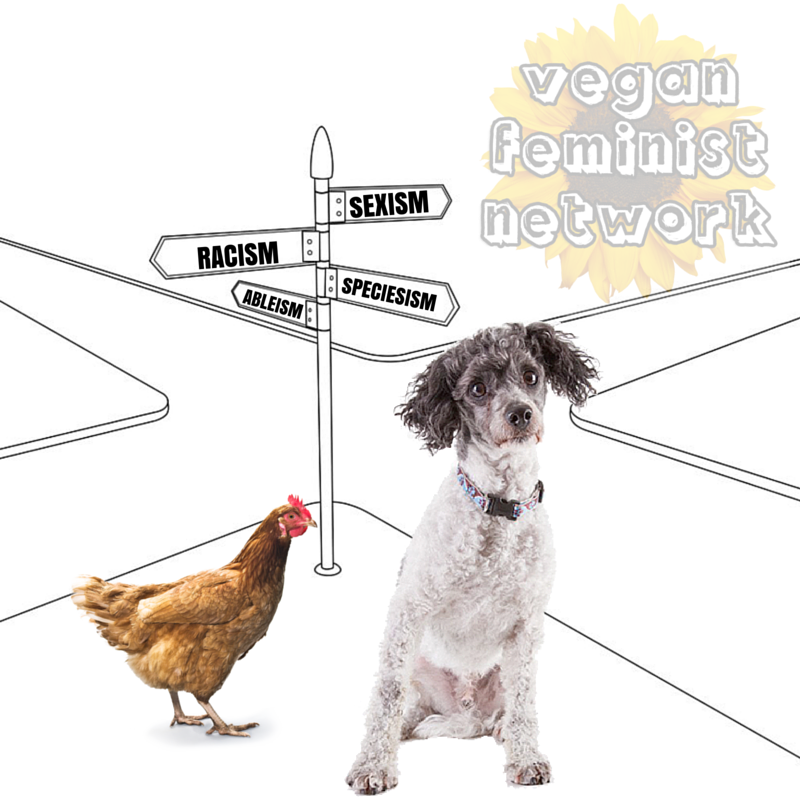
Given that species, class, race, gender, and other identity categories are all historically constructed using similar mechanisms (such as animalization, objectification, sexualization, depersonalization, denaming, and so on), it is important to apply an intersectional perspective to achieve a more accurate understanding of oppression for nonhuman animals and humans alike.
 Dr. Wrenn is the founder of Vegan Feminist Network. She is a Lecturer of Sociology and Director of Gender Studies with a New Jersey liberal arts college, council member with the Animals & Society Section of the American Sociological Association, and an advisory board member with the International Network for Social Studies on Vegetarianism and Veganism with the University of Vienna. She was awarded Exemplary Diversity Scholar 2016 by the University of Michigan’s National Center for Institutional Diversity. She is the author of A Rational Approach to Animal Rights: Extensions in Abolitionist Theory.
Dr. Wrenn is the founder of Vegan Feminist Network. She is a Lecturer of Sociology and Director of Gender Studies with a New Jersey liberal arts college, council member with the Animals & Society Section of the American Sociological Association, and an advisory board member with the International Network for Social Studies on Vegetarianism and Veganism with the University of Vienna. She was awarded Exemplary Diversity Scholar 2016 by the University of Michigan’s National Center for Institutional Diversity. She is the author of A Rational Approach to Animal Rights: Extensions in Abolitionist Theory.
