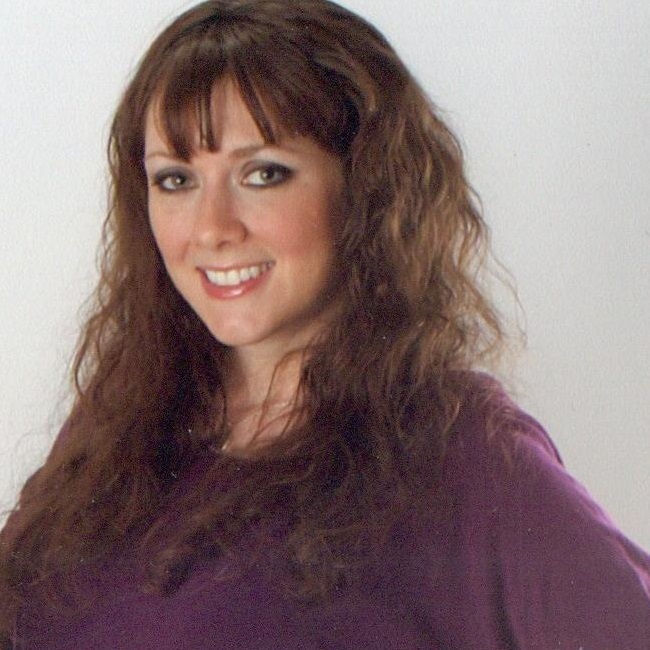
Photo Credit: Raymond Troumbly
By Z. Zane McNeill
People always assume that growing up queer in West Virginia was difficult, but I always tell them that I was bullied more for being vegan than being LGBTQIA+. I went vegetarian around the same time I realized that I had a crush on my best friend who was a girl. She was vegetarian too, and I was head over heels for her. At 14, I went vegan after learning more about factory farming and the suffering that is connected to dairy and egg production. In high school and early college, influenced by Carol Adams, Josephine Donovan, and Alice Walker, I was an adamant believer that in order to be a feminist I needed to be vegan. This later extended to queer liberation as intrinsically intertwined with animal liberation.
In my early 20s, I found queer community in Appalachia thanks to the zine, artist, and activist project Queer Appalachia. Through their social media accounts, I found other queer southern projects that I discovered, and subsequently collaborated and contributed to, like Bible Belt Queers, a community book project led by and for Southern queers, and Queering the Mountain, an art exhibition highlighting the work of Appalachian queers. Inspired by these, I eventually started my own zine project called Marx in the Mountains, have been working on a community book project on queer(ing) Appalachia, and have recently released a collection highlighting queer vegan voices around the world under Sanctuary Publishers, a resource activism focused vegan book publisher.
People who weren’t raised in this part of the world tend to not fully understand the way in which Appalachia is not simply a place. ‘Appalachia’ is in and of itself a contested definition. Appalachia is a space containing around 25 million people, or around 8% of the US population. It stretches through thirteen states following the Appalachian mountain range from New York to Alabama. Beyond a stretch of land, it is an area historically comprised of marginalized people—Indigenous folk, immigrants working for the coal companies, and other impoverished people tied into a form of serfdom in late-stage capitalism. In What You’re Getting Wrong About Appalachia, Elizabeth Catte explains that Appalachia is “a political construction, a vast geographic region, and a spot that occupies an unparalleled place in our cultural imagination.”[1] She herself is hesitant to label the concept of Appalachian identity and usually works with those who self-identify as Appalachian instead, as historically who self-identify as Appalachian instead, considering that, historically, who counted as Appalachian was decided by those in power or with massive amounts of capital. It is more than a geographic region—it is an environmental space with a history of toxicity from natural resource extraction, a cultural construction fashioned by conservatives to support revisionist arguments of what ‘America’ is and what bodies represent ‘America’, and a politically contested space that pushes disadvantaged voices to the margins.
When I was growing up in Appalachia, I was mostly bored but managed to pick up activism from my family. My stepfather was a well-traveled kayaker, and my mother was an HIV+ advocate in West Virginia. They were both schoolteachers, and I was lucky to grow up in the fun environment of music and books. However, to the dismay of the stepfather, I was more interested in reading Twilight than Marx. During the invasion of Iraq, my parents brought me with them to protests. The military practiced their maneuvers over our town, so my stepfather mowed a peace sign into our backyard. He delighted in knowing military pilots would gaze upon his anti-war protest while they performed their exercises. Both of my parents had a lot of gay friends and I was raised in the queer punk and art scenes in Morgantown—an environment a lot of people would be surprised existed in the mountains. Truthfully, growing up queer in West Virginia shaped my identity and understanding of self. I don’t feel the same way about my gender or sexuality as someone from the city might.
Coming to terms with being queer and coming out was awkward, but that was really it. In high school, when I came out as bi, I didn’t face discrimination—but people loved throwing their cafeteria food at me, showing me frogs they dissected, and stepping on bugs in front of me once they realized I was also vegan. At the same time, however, my friends and I had a Vegetarian Awareness Club and got a two-page spread in the yearbook. So, I would say that growing up vegan and queer in Appalachia was a weirdly empowering and isolating experience that informed my work in various animal welfare NGOs and queer grassroots organizing. My day-to-day life was continuously impacted by poverty, lack of transportation, and devastation by corporate greed. An area gutted by addiction, natural resource extraction, and neoliberalism left shadows on my friends’ faces and cuts on their arms. A lack of employment opportunities pushed the privileged out of the state to the cities, further pushing the marginalized into their homes with needles and pills. Being queer only makes sense to me with this as a backdrop. Constant violence has seemingly queered us all who are “from around here”.
I have seen progress as the years have passed, which is exciting in itself. In 2017, Queer Appalachia released the zine Electric Dirt, and since its release, a community of LGBTQIA+ folks from Appalachia, the South, and the Rust Belt has sprung up around it fighting to show that the discourse surrounding Appalachia leaves queer, Indigenous, Black, POC, femme, and leftist voices out. Queer challenges normative generalizations about the culture of Appalachia and explores how queer folks define themselves and the region “within the intersections of coal mines and class, race and religion, food justice and colonialism.” Queer Appalachia, as an overarching work, has benefitted the marginalized folk of Appalachia, giving a wide-ranging audience to those too often denied a platform. Yet, despite this progress, I still felt alienated by some of the content produced by the LGBTIQA+ Southern and Appalachian community. I was disappointed that collectives focused on the intersections between queer life, the opioid epidemic, the carceral system, Indigenous and Black liberation, and leftist organizing but did not also embrace animal welfare and veganism. This continued to shadow my experiences growing up queer and vegan.
In Appalachia, corporations see people as expendable, just as nonhumans are seen as objects to be used. I felt strongly about the work of scholar-activists like Dr. Breeze Harper, Adams, Julia Feliz Brueck, and Aph and Syl Ko who have illustrated that nonhuman oppression is inherently intertwined with our own. Specifically, Feliz Brueck coined the term ‘consistent anti-oppression’ to describe how marginalizations are inherently connected and should be equally fought against, which makes sense to me.
Fueled by this framework, I approached Feliz Brueck, who also runs Sanctuary Publishers, about an anthology that would invite folks who identified at LGBTQIA+ and vegan to meditate on how their identities intersect, how being LGBTQIA+ affects their vegan activism, and what they would like to say to non-vegan LGBTQIA+ folk. The end result, which was recently released, was a book project that includes over 25 contributors—activists, scholars, artists, and writers who identify as LBTQIA+ and vegan—who explored the interconnections between social justice groups, building bridges between movements, and dismantling hierarchies between oppressed groups through consistent anti-oppression in this volume. In the book, known activists like Jasmin Singer speak about their initial work with AIDS Awareness, while scholar Margaret Robinson discusses how veganism ties into her decolonization as a two-spirit person, and Shiri Eisner speaks to her journey of coming out as a bisexual, genderqueer Mizrahi vegan. However, the focus is not on known activists, and that’s what makes this book and the work of Sanctuary Publishers different. Voices often denied a platform are able to have one if they choose to in written form.
Growing up queer and vegan in Appalachia was an experience that challenged metronormative stereotypes—happily queer in the holler, organizing Earthlings showings in West Virginia, and going on queer dates to a vegan-friendly co-op. Yet, I find a special kind of comfort knowing that those in other parts of the world from different cultures and life journeys understood me in a way that I had not felt before. Since embarking on the road to publish the queer vegan anthology, I found myself validated in both these identities—being vegan and queer—and in recognizing that they were always inherently connected to me, and that being vegan has informed my queer activism and vice versa. Queer vegans across the globe share this sentiment, perhaps because we have historically faced an otherization that has led to our own violence and marginalization.
I hope that vegans recognize the importance of embracing a veganism that is consistently against all oppression in an effort to ensure we recognize that the movement has work to do regarding how we avoid marginalization of others at the expense of nonhumans. I also hope that non-vegan LGBTQIA+ folks, especially my friends in the queer Appalachian community, recognize that our marginalization extends to others through our daily choices, and that in order to fight for our queer liberation, we must also fight for nonhuman animal rights.
[1] Catte, Elizabeth. What You Are Getting Wrong about Appalachia. Cleveland, OH: Belt Publishing, 2018, 10.
Zane McNeill is an independent scholar-activist from Appalachia. Their newly published book Queer and Trans Voices: Achieving Liberation Through Consistent Anti-Oppression edited by themselves and Julia Feliz Brueck explores the interconnections between social justice groups in order to consistently and effectively achieve liberation for all.
You can read more on intersections of queer activism and veganism in Queer and Trans Voices, available for purchase through Amazon website or Sanctuary Publishers Instagram.