TRIGGER WARNING: This essay contains a frank discussion of rape analogy in the Nonhuman Animal rights movement, including images that depict violence against women. There are also discussions of other forms of human suffering (like pedophilia and racism) that may be painful for some readers.

In this essay, I want to quickly address some common responses to Vegan Feminist Network’s position on misogynistic imagery as a tactic in Nonhuman Animal rights. I believe much of the response reflects a commitment to sexism, but some also reflects a general ignorance to the impact that patriarchal ideology and a social environment of misogyny has on the activist imagination. The response also reflects a need to deflect discomfort, because these are tactics that have come to dominate our social movement space, and many have taken them for granted as acceptable and useful. Being made aware of participation in violence triggers cognitive dissonance, and it is a natural response to debate, deride, or deflect in order to protect a positive self-concept.
One of the most common responses we receive is an appeal to alternatives (the implication being that alternatives are either too difficult to imagine or simply do not exist). Activists may be sincere in their inquiries for alternatives to misogynistic tactics, but I believe this response is often engaged to derail the discussion. All activists know that there are certain lines that should not be crossed because they will be so offensive that they will hurt others and repel participants.1 We don’t want to cause hurt and we want to grow our movement, so analogies that go too far are inappropriate.

Just today, this image was shared by A Well Fed World and Free From Harm. While no women are pictured, the analogy is implicit. Research into morally shocking imagery suggests that this approach can easily repel audiences. We can imagine how this response would be magnified by female audiences that are triggered by images of sexual assault and rape.
More and more activists in the movement recognize that slavery and Holocaust analogies are problematic. True, there are still some white-identified/non-Jewish persons clinging onto these analogies, but there are other analogies that I daresay no one would get behind. For instance, I think it is fair to say that everyone agrees that pedophilia analogies would go too far. A common analogy between women and other animals involves the violence of dairy production. Women are often depicted as being assaulted, beaten, and raped to make a point about what happens to cows. When women are targeted, there seems to be little objection. However, if activists were to produce and promote memes of children being sexually assaulted to raise awareness to dairy cows being violated, most would have to agree that this approach would be so triggering and hurtful, that it would be an act of violence and would put the movement in a bad light. Indeed, because the cows in the dairy industry are still babies and children themselves when they are hoisted onto the industry-termed “rape rack,” wouldn’t pedophilia analogies be more accurate than those that draw on violence against adult women?
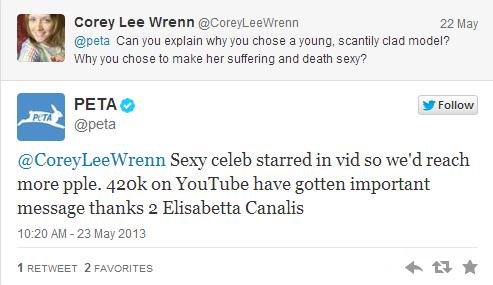
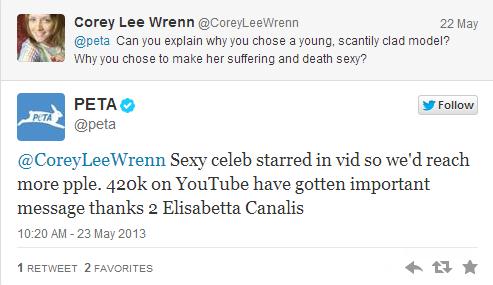
But it isn’t about accuracy. It’s about swapping out one degraded and worthless body for another. As one reader pointed out, PETA’s foie gras campaign that positions women as the duck victim in advertisements and demonstrations across the world is illogical because ducks used in the industry are male. That doesn’t stop PETA from “telling it like it is.”






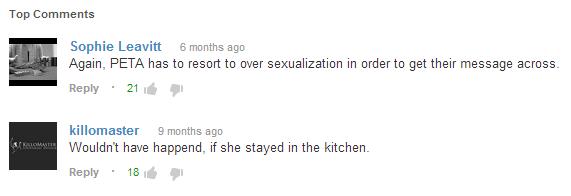
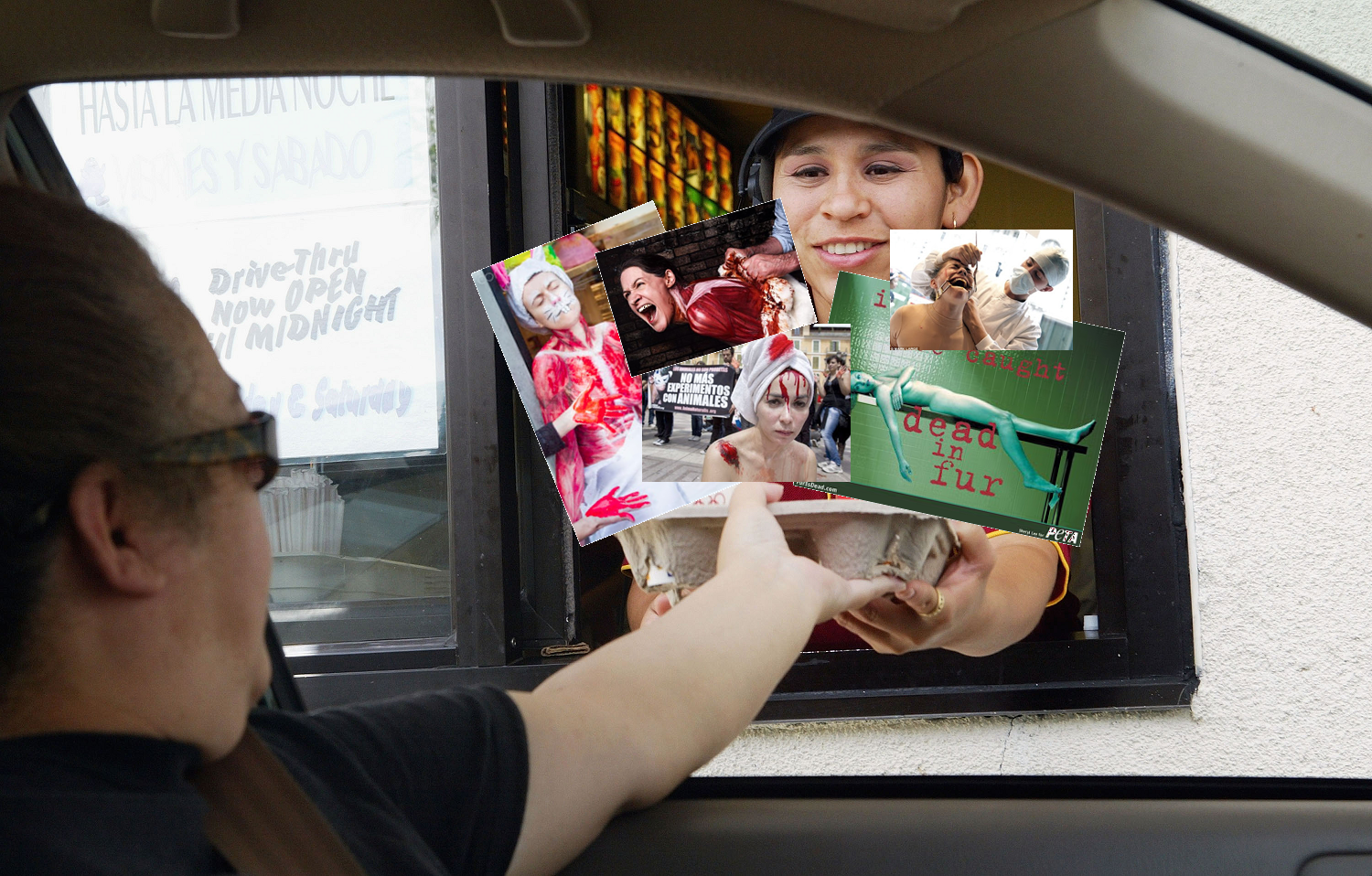
Indeed, a common response to misogynistic analogies is that “this is accurate; this is how it really is.” Vegan Feminist Network isn’t arguing against that, but we must be cognizant of media as a social construction. Media creators choose what story they want to tell and they seek to manipulate how audiences will interpret them. We live in a rape culture where violence against women is commonplace. The movement draws on this social reality to trigger a specific response. Patriarchal ideology may make many unconscious to this language they are using, but activists are not ignorant. No one (I hope) uses images of lynching or violence in nursing homes or mental institutions. No one uses images of humans with deadly diseases like cancer, AIDS, or ebola. All of these human experiences with violence and suffering could easily be enacted to make analogies about Nonhuman Animal exploitation. Fortunately, activists know better than to use them, because it is understood that they will be offensive and painful to the vulnerable groups whose experiences are appropriated. Except for women. The movement produces thousands of images and reenactments of women bloodied, bruised, assaulted, raped, dying and dead. Because women don’t count.
Women are still at the bottom of the ladder. Violence against women is so commonplace, it is rarely even questioned as a painful subject in the Nonhuman Animal rights movement. This is to be expected. In all social movements, women have been ignored, exploited, and left behind.2 The anti-slavery movement would not let women participate and intentionally excluded gender from campaigns to make legislative language more inclusive. The Civil Rights movement kept women in organizational roles and pushed men into the leadership positions. The gay rights movement seriously underserved lesbians. The free-thinking/atheist movement soundly denies the need to recognize feminist issues. In all efforts to advance social justice, women have been made to take a back seat, never considered fully equal or worthy of rights. The feminist movement has been seeking to challenge this ideology since women were first ousted from anti-slavery efforts in the 1800s, but female activists continue to be framed as loudmouthed, unattractive, mentally unstable, feminazis. Just last month, Time Magazine listed the word “feminist” on their reader poll of words that should be banned. We’ve come a long way baby…but not nearly far enough.
Sexism is so normalized in our society that it has become invisible. You cannot turn on the television without being exposed to sexist remarks, jokes at women’s expense, sexual harassment, sexual objectification, and violent assault and rape of women. We are all exposed to a nonstop onslaught of sexist imagery in our society. It becomes as natural as the air we breathe. The bodies of women have always been sites of violence and domination, to the point where it becomes mundane and expected. So, when Vegan Feminist Network takes a stand against the encroachment of this violent imagery in Nonhuman Animal rights spaces, readers are understandably taken aback. They’ve never been made to think critically about the gender-based violence they have taken for granted as acceptable and normal for all of their lives.
Readers often respond with disbelief or with weak justifications, demanding a soundbite explanation as to why this behavior is problematic in two Facebook comments or less. The information is out there (as just one example, the Vegan Feminist Network website is chock full of free information), but few really want to learn more, because I suspect that few really care. This is the way it has always been done, women are easy targets, and women’s pain doesn’t matter (or matters less).
Kim Socha refers to these kinds of trans-species tactics as “fast food activism.” There is no concern with investigating why these analogies might be problematic, that is, why they may not work as a scientific matter, how the state of sexism is in our society influences interpretation, or how they impact women. Just like McDonalds, these analogies pull on the readily available language of violence against women and pump out advocacy cheaply and quickly irrespective of the hurt it causes to vulnerable groups and the damage done to society.
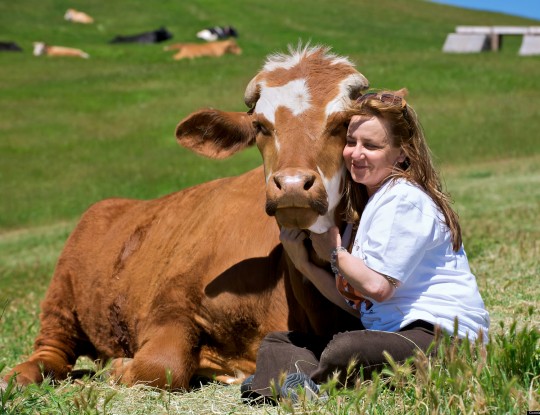

Violence-free activism that brings attention to Nonhuman Animal exploitation and the intersectionality of oppression is not difficult to achieve.
There are tons of ways we can help other animals without resorting to this tokenizing approach. I’ve published hundreds of essays on this website and on my personal blog, The Academic Abolitionist Vegan, most of which are grounded in my research in social movement theory and social psychology, and all of which are freely available. There are also hundreds of books on effective social change available. There’s no excuse for allowing patriarchal norms and PETA’s influence to dictate our activism. We don’t need to hurt women to help animals. We do it because it is easy and because women don’t matter, and that is a problem.
Notes
1. There are a few exceptions, including Israeli group 269Life which, in addition to “reenacting” sexual assault and violence against women in public, also uses shackles, chains, and branding on humans in street demonstrations. PETA, too, has utilized graphic analogies of African slavery and the Holocaust.
2. This is not to say that women were not leaders and important players (in all movements there are important exceptions), but only to emphasize that movements act as microcosmic social systems and too often exclude women and ignore their interests.
 Dr. Wrenn is Lecturer of Sociology. She received her Ph.D. in Sociology with Colorado State University in 2016. She received her M.S. in Sociology in 2008 and her B.A. in Political Science in 2005, both from Virginia Tech. She was awarded Exemplary Diversity Scholar, 2016 by the University of Michigan’s National Center for Institutional Diversity. She served as council member with the American Sociological Association’s Animals & Society section (2013-2016) and was elected Chair in 2018. She serves as Book Review Editor to Society & Animals and has contributed to the Human-Animal Studies Images and Cinema blogs for the Animals and Society Institute. She has been published in several peer-reviewed academic journals including the Journal of Gender Studies, Feminist Media Studies, Disability & Society, Food, Culture & Society, and Society & Animals. In July 2013, she founded the Vegan Feminist Network, an academic-activist project engaging intersectional social justice praxis. She is the author of A Rational Approach to Animal Rights: Extensions in Abolitionist Theory (Palgrave MacMillan 2016).
Dr. Wrenn is Lecturer of Sociology. She received her Ph.D. in Sociology with Colorado State University in 2016. She received her M.S. in Sociology in 2008 and her B.A. in Political Science in 2005, both from Virginia Tech. She was awarded Exemplary Diversity Scholar, 2016 by the University of Michigan’s National Center for Institutional Diversity. She served as council member with the American Sociological Association’s Animals & Society section (2013-2016) and was elected Chair in 2018. She serves as Book Review Editor to Society & Animals and has contributed to the Human-Animal Studies Images and Cinema blogs for the Animals and Society Institute. She has been published in several peer-reviewed academic journals including the Journal of Gender Studies, Feminist Media Studies, Disability & Society, Food, Culture & Society, and Society & Animals. In July 2013, she founded the Vegan Feminist Network, an academic-activist project engaging intersectional social justice praxis. She is the author of A Rational Approach to Animal Rights: Extensions in Abolitionist Theory (Palgrave MacMillan 2016).